Around 60%–70% of all primary health care visits in developed countries are for lifestyle-based (and therefore preventable) diseases.1 Although lip service is often paid to prevention,2 governments of all persuasions have largely neglected the funding of real preventive action. Hence, while not giving up on Geoffrey Rose’s epidemiological dictum that small changes in large populations are likely to be more effective than large changes in small numbers,3 it is evident that a change is needed in the management of modern chronic diseases. This new approach needs to bridge the gap between public health, with its preventive and population-based aims, and the treatment and patient-centred focus of clinical practice. The advent of a modified clinical discipline — “lifestyle medicine” — offers a way to bridge this gap.
We have defined lifestyle medicine as “the application of environmental, behavioural, medical and motivational principles to the management of lifestyle-related health problems in a clinical setting”.4 The discipline involves the therapeutic use of lifestyle interventions predominantly in the management of chronic disease.
First developed in the United States,5 lifestyle medicine is taught in specialist postgraduate medical training courses in at least three US universities (Harvard, University of Florida and Loma Linda). There are currently several specialist lifestyle medicine associations and a journal, the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
The adoption of the Enhanced Primary Care (EPC) system in Australia,6 which allows Medicare benefits for 13 allied health disciplines involved in the management of chronic disease, as well as enhanced benefits for general practitioners, provides a wider scope for lifestyle medicine than in the US. Although it is not without drawbacks,7 the EPC system is evolving into an effective means of dealing with chronic diseases that do not easily remit under conventional pharmaco-medical management and that are the by-product of societal changes including improved standard of living and economic circumstances.
Lifestyle medicine, like clinical practice, employs deductive reasoning but draws on a wider range of causal factors than is usually considered in a traditional clinical setting. Box 1, for example, shows that chronic diseases have risk factors and markers, which are often the focus of clinical intervention. However, these factors and markers have causes that can be “proximal”, “medial” and “distal” to the disease. Pharmaco-medical treatments for chronic, lifestyle-related disease — while necessary and important — should not be accepted as a complete solution to the problem.
A more comprehensive approach to the management of chronic disease would consider not only risk factors, but also a range of antecedent factors from all levels of causality. Treatment would ultimately employ a combination of clinical and public-health interventions, which may not always seem intuitive. For example, population rates of obesity could be reduced by not only implementing personal weight-loss programs at the clinical level, but also highlighting the environmental effects of burning fossil-fuel instead of personal energy for transport.8
Several large-scale prospective studies have now shown the benefits of lifestyle change in preventing progression from pre-diabetes to type 2 diabetes,9-11 with effects lasting for up to 20 years.10 Cost-effectiveness has also been demonstrated.12
Lifestyle medicine, with its concentration on several levels of causality in disease, differs in orientation to conventional clinical practice (Box 2). In particular, there is a requirement for the patient to be more active in his or her own care. Because of the often large behavioural and emotional “cost” and commitment required to make lifestyle changes, a deeper understanding of motivational principles is needed, and the coordinating physician could use the expertise of allied health disciplines (Box 3). Yet there is little in the medical literature or at medical conferences to assist clinicians in understanding practical approaches to motivate patients. Funding for research programs remains heavily weighted in favour of pharmacological solutions. Motivational interviewing13 is a relatively rare example of a non-pharmacological technique that is commonly used in clinical practice.
Medication, in the lifestyle-medicine paradigm, is seen more as an adjunct than an end treatment in care, and side effects are recognised as part of the outcome. Erectile dysfunction from anti-depressant medication in middle-aged men, for example, can potentially exacerbate depression. Hence this effect should be weighed against the possible benefits of a lifestyle-change option such as exercise, for which a strong evidence base in managing depression exists.14
Many lifestyle behaviours that cause chronic disease seem to be closely linked in vicious cycles, and an underlying cause may be the low-grade systemic inflammation now identified as being associated with lifestyle-related diseases.15 Inadequate sleep, for example, can lead to fatigue; fatigue to inactivity; inactivity to poor nutrition or overeating; and all of these factors can exacerbate obesity and depression, leading to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, sexual dysfunction and mood problems, and potential heart disease. Medication can help manage many of these problems, but, as discussed earlier, may also cause counterproductive side effects such as weight gain, exercise-induced myopathy,16 and sexual dysfunction. All of these — the predisposing factors, cause, disease and treatment — make up the practice of lifestyle medicine, which, in an ideal world, would be supported by effective and sustained public health efforts.
Evidence to date suggests significant cost benefits of lifestyle medicine,12 but long-term prospective assessment is required. Meanwhile, lifestyle-related chronic diseases are unlikely to decrease in the near future. Hence, the prospects for a discipline of lifestyle medicine indeed appear healthy.
1 A hierarchy of causes of chronic disease4*
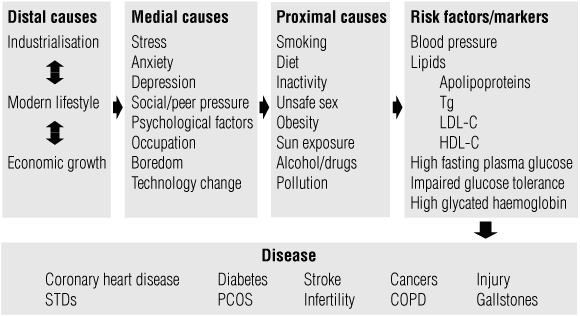 | |||||||||||||||
* From Egger et al. Lifestyle medicine . Sydney: McGraw-Hill Australia, 2008: 16. | |||||||||||||||
- Garry J Egger1,2
- Andrew F Binns2,3
- Stephan R Rossner4
- 1 Centre for Health Promotion Research, Sydney, NSW.
- 2 Southern Cross University, Lismore, NSW.
- 3 Lismore, NSW.
- 4 Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
Garry Egger coordinates and Andrew Binns has contributed to a postgraduate Master of Clinical Science (Lifestyle-Medicine) program through Southern Cross University. Andrew Binns is the president of ALMA and Garry Egger is an ALMA committee member.
- 1. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Chronic diseases and associated risk factors in Australia, 2006. Canberra: AIHW, 2006. (AIHW Cat. No. PHE 81.)
- 2. Australia 2020 Summit: long-term health strategy. http://www.australia2020.gov.au/topics/docs/health.pdf (accessed Nov 2008).
- 3. Rose G. The strategy of preventive medicine. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1992.
- 4. Egger G, Binns A, Rossner S. Lifestyle medicine. Sydney: McGraw-Hill Australia, 2008.
- 5. Rippe J, editor. Lifestyle medicine. New York: Blackwell, 1999.
- 6. Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing. Enhanced Primary Care Program (EPC). http://www.health.gov.au/epc (accessed Nov 2008).
- 7. Beilby JJ. Primary care reform using a layered approach to the Medicare Benefits Scheme: unpredictable and unmeasured. Med J Aust 2007; 187: 69-71. <MJA full text>
- 8. Egger G. Personal carbon trading: a potential “stealth intervention” for obesity reduction? Med J Aust 2007; 187: 185-187. <MJA full text>
- 9. Herder C, Peltonen M, Koenig W, et al. Systemic immune mediators and lifestyle changes in the prevention of type 2 diabetes: results from the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Diabetes 2006; 55: 2340-2346.
- 10. Li G, Zhang P, Wang J, et al. The long-term effect of lifestyle interventions to prevent diabetes in the China Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Study: a 20-year follow-up study. Lancet 2008; 371: 1783-1789.
- 11. Haffner S, Temprosa M, Crandall J, et al; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Intensive lifestyle intervention or metformin on inflammation and coagulation in participants with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2005; 54: 1566-1572.
- 12. Galani C, Schneider H, Rutten FF. Modelling the lifetime costs and health effects of lifestyle intervention in the prevention and treatment of obesity in Switzerland. Int J Public Health 2007; 52: 372-382.
- 13. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational interviewing: preparing people for change. London: Guilford Press, 2002.
- 14. Barbour KA, Edenfield TM, Blumenthal JA. Exercise as a treatment for depression and other psychiatric disorders: a review. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev 2007; 27: 359-367.
- 15. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disease. Nature 2006; 444: 860-867.
- 16. Sinzinger H, O’Grady J. Professional athletes suffering from familial hypercholesterolaemia rarely tolerate statin treatment because of muscular problems. Brit J Clin Pharmacol 2004; 57: 525-528.






Abstract
Chronic diseases with a lifestyle-based aetiology currently make up a significant proportion of primary care consultations, but management often falls between the demands of public and clinical health.
A modified clinical approach, based around the concept of “lifestyle medicine”, helps fill the gap by adding behavioural, motivational and environmental skills to conventional medical practice.
When used in a multidisciplinary setting, lifestyle medicine offers potential cost and effectiveness benefits, which are beginning to be realised.