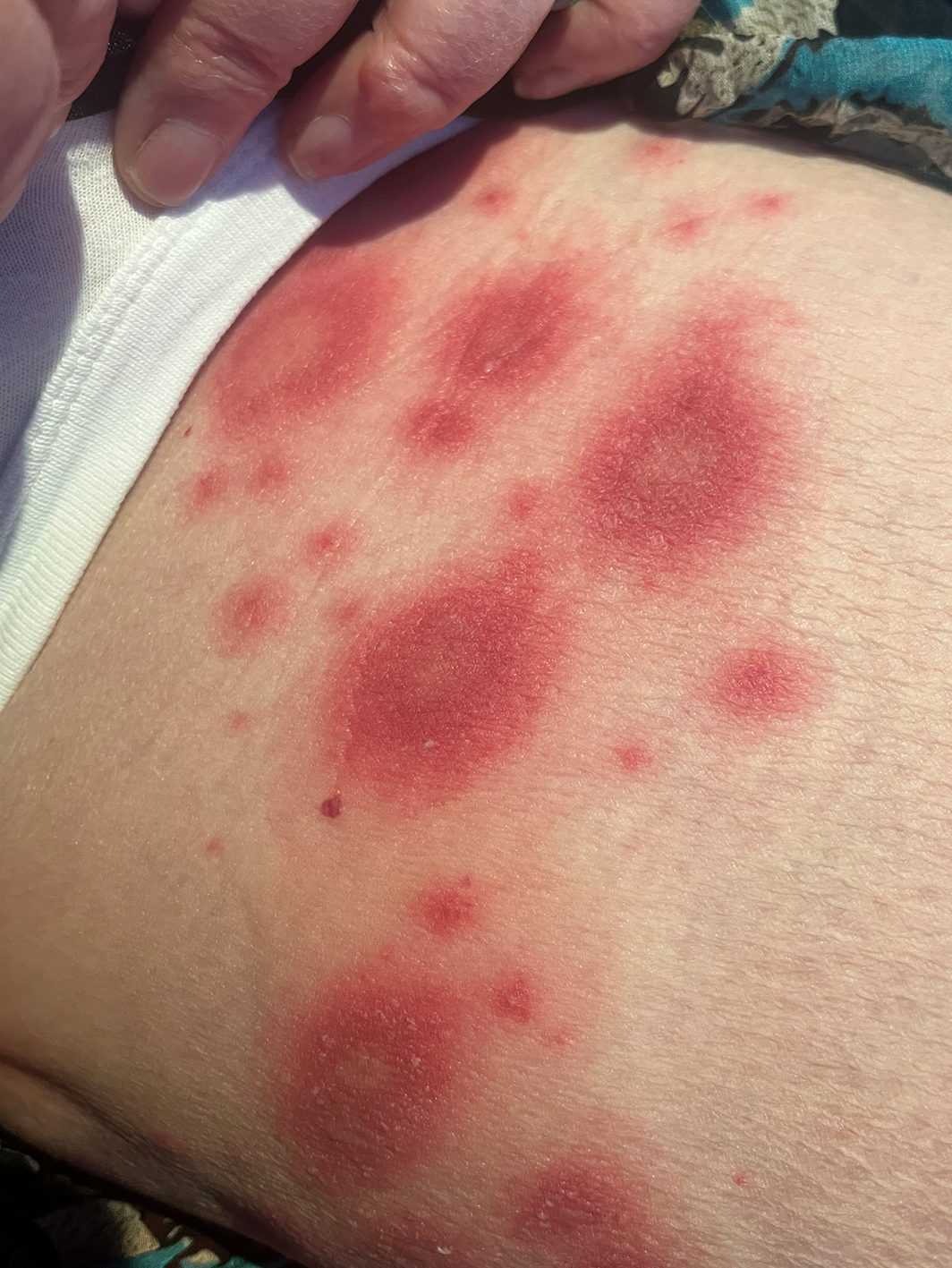
A 65‐year‐old woman presented to the emergency department with asymptomatic plaques on her left medial thigh. She had commenced amoxicillin–clavulanate for facial cellulitis the evening prior. On examination, she displayed multiple well defined oval erythematous plaques with variable central vesiculation (Figure). A skin biopsy showed a lichenoid reaction pattern, and a fixed drug eruption was diagnosed. Fixed drug eruption is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction that generally manifests as a solitary, or small group of lesions, 30 minutes to eight hours after drug administration. It characteristically recurs in the same location upon re‐exposure to the culprit drug, and recurrences can be increasingly severe and even generalised.1 Analgesics such as paracetamol, non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs, antibiotics including tetracyclines, antibacterial sulfonamides, and hypnotics are among the most frequent causes.2 Treatment is discontinuation and avoidance of the offending drug.
The full article is accessible to AMA
members and paid subscribers.
Login to MJA or subscribe now.
- 1. Patel S, John AM, Handler MZ, Schwartz RA. Fixed drug eruptions: an update, emphasizing the potentially lethal generalized bullous fixed drug eruption. Am J Clin Dermatol 2020; 21: 393‐399.
- 2. Mahboob A, Haroon TS. Drugs causing fixed eruptions: a study of 450 cases. Int J Dermatol 1998; 37: 833‐838.





No relevant disclosures.