Osteoarthritis is the leading cause of pain and disability among the elderly and affects 15% of the population. Despite a range of treatments for osteoarthritis (OA), joint replacement remains the main treatment option for patients in whom the disease has progressed.1
In Victoria, more than 20 000 hip and knee joint replacements are now performed each year, reflecting orthopaedic practices globally. The prevalence of OA and the need for joint replacement are likely to increase because of a combination of increasing risk factors (age, obesity) and improved surgical and anaesthetic techniques that make surgery possible for more people.1
Across health services, there is wide variation in hospital length of stay for patients receiving hip and knee replacements. This is probably independent of casemix and more reflective of varying health service practices. Surgical injury, pain, stress-induced catabolism, impaired organ function and impaired cognitive function may contribute to complications, prolonged hospitalisation, postoperative fatigue, delayed convalescence and the need for rehabilitation. Optimisation of individual care components in perioperative care (the fast-track methodology) reduces the need for prolonged hospitalisation and convalescence, and reduces morbidity, with subsequent economic savings.2-6 Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) programs are a care package of evidence-based interventions used in a multimodal, integrated clinical care pathway to achieve improved functional outcomes and rapid recovery.6 ERAS pathways have led to reduced hospital stays after hip or knee replacements — as short as 3 days in many centres.5-8
We aimed to assess the extent to which a predefined ERAS program for orthopaedic surgical patients could be achieved, and to evaluate improvements in quality of care and patient outcome across three public hospitals in Victoria.
Methods
We used a before-and-after study design consisting of three phases. Public health services involved in the study were the Alfred, Bendigo and Monash hospitals.
Phase 1: over the 6 months before implementation of the ERAS program, we recorded perioperative data for all eligible patients undergoing surgery (the existing-practice cohort).
Phase 2: training of staff managing orthopaedic surgical patients. For 1 month, the evidence-based background to ERAS was promulgated to all surgical, anaesthetic and nursing staff. This was done in various forms including lectures, workshops, meetings and written instructions.
Phase 3: change performance. We undertook a repeat audit following the implementation of the ERAS care package (the ERAS cohort).
Our study received ethics approval as an audit project with a waiver for specific patient consent (Alfred Human Research Ethics Committee, EC 92/12).
The pre-ERAS phase ran from March to September 2012. Training of staff took place over September 2012. The ERAS phase ran from October 2012 to May 2013.
Patient health status was quantified using the American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification, ranging from 1 (healthy patient) to 5 (moribund patient not expected to survive without the operation). Patient quality of recovery was assessed using the patient-centred, 15-item quality-of-recovery score,9 and the 12-item World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 score.10 Indicators of patient satisfaction were assessed at 30 days after surgery using a 5-item Likert scale (0 = strongly agree, 5 = strongly disagree).
Actual hospital stay was timed from the beginning of surgery until discharge. We evaluated readiness for discharge on postoperative Day 3, defined by whether patients were eating and drinking, had no drain tubes or urinary catheters, were weight-bearing, and had well controlled pain scores (visual analogue scale with a range of 0 to 10) at rest and on movement of less than 3 and 5, respectively.
A successful ERAS implementation required at least 11 of 16 prespecified ERAS items (Box 1).
On completion of our study, there was a concern raised by the surgical team at the lead institution regarding an apparent increased incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI). In view of the widespread use of local anaesthetic infiltration with a solution that included ketorolac 30 mg, we chose to investigate this more formally at the lead institution. We retrospectively retrieved all perioperative creatinine data for the study cohorts. AKI was defined according to AKI Network11 and RIFLE (risk, injury, failure, loss, end-stage kidney disease)12 criteria. We did not include urine output or oliguria in the definitions of AKI, in part because we did not collect these data, but primarily because urine output is an unreliable indicator of renal function in the perioperative setting.
To account for the restrictive intravenous (IV) fluid regimen used in the ERAS cohort (which may have artificially elevated serum creatinine because of the avoidance of a dilutional effect from excessive IV fluids increasing body water), we calculated the adjusted creatinine concentration by first estimating the volume of distribution for creatinine as equal to total body water (assumed to be 60% of body weight, expressed in mL), and assuming that 50% of IV fluid was still accumulated as tissue oedema at the time of postoperative creatinine measurements:13
adjusted creatinine concentration = serum creatinine concentration × (1 + [0.5 × IV fluid balance/total body water])
Analysis of the data showed that there was no increased incidence of AKI in the ERAS group (Appendix 1).
The primary end point of the study was duration of hospital stay. Secondary end points were adherence to the ERAS bundle (defined as ≥ 11 items), and a number of patient outcome measures. A sample size calculation based on a change in hospital stay from a mean of 7 days (SD, 4 days) to 6 days (SD, 3 days), with an α value of 0.05 and a β value of 0.2, required at least 380 patients to be enrolled, but we included a larger sample in view of the planned subgroup analyses. Continuous data are reported as mean (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR). Numerical data were first tested for normality using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test and then compared using the Student t test or Wilcoxon rank–sum test, as appropriate. Rates were compared using χ2 or Fisher exact test, as appropriate. Hospital stay was expected to be skewed to the right because of a small proportion experiencing complications and a protracted hospital stay. Therefore, we log-transformed hospital stay data to enable valid comparison using the t test; in addition, we report median (IQR) length of stay and results of Wilcoxon rank–sum testing. Patients undergoing each type of surgery were also analysed as subgroups. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data were analysed with SPSS version 20.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc).
Results
We enrolled 709 patients into the project; 412 in the existing-practice cohort and 297 in the ERAS cohort (Box 2). We achieved 100% patient follow-up to hospital discharge and 90% follow-up at 6 weeks; there were 41 (10%) and 25 (8%) patients missing in each cohort, respectively. Comparison of data from the three hospitals showed that the patients were similar demographically as well as having similar rates of physical functioning and comorbidity. The existing-practice and ERAS cohorts, with the exception of some medications, were comparable (Box 2), which allowed unadjusted analyses between groups.
The ERAS program led to a significantly higher rate of successful implementation of this clinical pathway (2% v 81%; P < 0.001) (Box 3, Box 4, Box 5 and Appendix 2). The post-implementation cohort had a significantly increased number of ERAS interventions compared with the existing-practice group (median, 12 [IQR, 10–13] v 8 [IQR, 7–10]; P < 0.001).
Overall, there was a significant reduction in hospital stay (geometric mean, 5.3 [SD, 1.6] v 4.9 [SD, 1.6] days [P < 0.001]) (Box 4), with around half of the patients being discharged from hospital within 5 days of surgery (ERAS group, 60% v existing-practice group, 52%; P = 0.086). For those undergoing knee replacement surgery, the ERAS program was associated with a reduced hospital stay (geometric mean, 5.3 [SD, 1.6] v 4.5 [SD, 1.5] days [P = 0.001]; median, 5.0 [IQR, 4.0–6.7] v 4.1 [IQR, 3.0–6.0] days [P = 0.005]); and a greater proportion of patients were more likely to be discharged by Day 5 (64% v 52%; P = 0.019). There was no change in median hospital stay for hip replacement patients in the ERAS group compared with the existing-practice group (median, 5.0 [IQR, 3.5–7.0] v 5.0 [IQR, 4.0–6.9] days; P = 0.99). Overall, the 75th centile for length of stay decreased from 6.8 to 6.0 days.
We found high rates of compliance with nearly all ERAS items (Box 3). There was increased use of spinal anaesthesia. The use of femoral nerve block (with or without a catheter) was substituted by favouring surgeon-delivered local anaesthetic infiltration in 75% of cases; this change in practice varied across the three hospitals (98%, 37% and 98%). There were improved dynamic pain scores and quality of recovery (Box 4). There were improvements in other recovery parameters (early feeding, ambulation and removal of tubes). Patients undergoing knee replacement had improved flexion on postoperative Days 1 and 2.
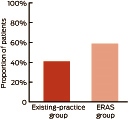
The proportion of patients ready for discharge on Day 3 after surgery was significantly higher in the ERAS group compared with the existing-practice group: 59% v 41%, respectively; relative risk, 1.35 (95% CI, 1.18–1.53); P < 0.001 (Box 6 and Appendix 1).
The 6-week complication rates were similar and there was no increase in the rate of hospital readmission. Pain levels were similar and there was a higher level of patient satisfaction at 6 weeks after surgery (Box 5).
The incidence of AKI was comparable between groups (Appendix 1). The final plasma creatinine values were slightly higher in the ERAS group, but this could be accounted for by higher baseline (preoperative) values; ERAS patients had a mean change in creatinine from 78 mmol/L (SD, 24 mmol/L) preoperatively, to a final reading of 79 mmol/L (SD, 24 mmol/L) postoperatively. There were no cases of renal failure.
Discussion
Our study results indicate that implementing an ERAS program may be beneficial for other Victorian public hospitals. The ERAS program had a small but significant effect on hospital stay, particularly for knee replacement patients. A pertinent finding from our study was that a higher proportion of patients managed through the ERAS care pathway compared with the existing-practice group (59% v 41%, respectively) were deemed ready for discharge on postoperative Day 3.
The limited effect on actual hospital stay in this project is likely to be due to one key factor: despite an effectively implemented ERAS program, there were entrenched hospital practices that prevented earlier hospital discharge even though patients were deemed ready for discharge; that is, discharge planning practice was mostly unchanged. This is due to established ward practices, including a repetitive requirement for many joint replacement patients to undergo their initial rehabilitation program as an inpatient (delaying their discharge). Patients referred for rehabilitation often wait for some time (hours or days) before being reviewed by rehabilitation services. Further, if surgery occurred on a Thursday or Friday, patients had minimal access to physiotherapy over the weekend. These aspects offer opportunities for improvement. The challenge is clear: to convert improvement in care (and outcome) into shorter hospital stay.
Our primary end point was duration of hospital stay. As we have done previously,14 we used a log-transformation and compared geometric means to account for skewness of our data (a small proportion of patients staying in hospital for very long times distorts central tendency — a well known phenomenon for many types of surgery). A secondary non-parametric comparison of median stays was not statistically significant. Therefore, we reported the 75th centiles to illustrate the observed improvement in hospital stay for the majority of patients.
Administrative and traditional patterns of clinical practice limit opportunities for change and are common causes of delayed discharge from hospital.14-16 Perhaps specific fast-track arthroplasty units that have evidence-based and protocolised rapid recovery pathways can optimise cost-efficient quality outcomes after hip and knee replacement surgery.15 This could reduce hospital costs, improve patient satisfaction with care and potentially reduce perioperative morbidity.
We demonstrated that an ERAS program for orthopaedic joint replacement can be achieved. We markedly improved most indicators of processes related to an ERAS program. These included preadmission patient education, reduced fasting times, clear oral fluids, written instructions (including expected day of discharge), less blood loss, better pain relief, earlier ambulation and better overall quality of recovery. Similar success has been reported in other countries.8,17,18 Medical teams can be trained to deliver an ERAS program and this clearly improves the quality of care.
We clearly demonstrated that we could successfully implement a predefined ERAS program for orthopaedic surgical patients in public hospitals, and that doctors and nurses could follow such a regimen to improve outcome parameters. There was high uptake of nearly all ERAS items. This led to clinically important improvements in care, a small reduction in hospital stay for knee replacement patients, and an overall improvement in some aspects of patient satisfaction. There was evidence of improved quality of recovery. There was no effect on most complications and no adverse effect on hospital readmission rates.
Our 6-week complication rates are lower than those reported in most studies, the largest of which included 4500 consecutive unselected hip and knee replacements.5 In that study, the first 3000 patients represented existing or traditional practice and a further 1500 patients underwent an ERAS protocol similar to that used in our study. This group reported a decrease in length of stay from 6 days to 3 days (P < 0.001), as well as a reduction in 30-day mortality (from 0.5% to 0.1%; P = 0.02) and 90-day mortality (from 0.8% to 0.2%; P = 0.01). Blood transfusion was reduced from 23% to 9.8% (P < 0.001). There was a trend of a reduced rate of 30-day myocardial infarction (from 0.8% to 0.5%; P = 0.2) and stroke (from 0.5% to 0.2%; P = 0.2). There was no measurable effect on deep vein thrombosis (0.8% v 0.6%; P = 0.5) or pulmonary embolism (1.2% v 1.1%; P = 0.9).
There were some limitations of our study. It was not a randomised trial and there may have been some imbalance between the groups that we did not account for. The study was unblinded and we compared numerous secondary end points. Although there are likely to be cost benefits of an ERAS program, we did not undertake any health costing analyses.
We found a high level of general acceptance and uptake of the ERAS program and, on the whole, it had a positive effect on patients and staff. We can recommend this orthopaedic ERAS pathway.
Anchor
2 Patient demographic and perioperative characteristics*
Variable | Existing practice (n = 412) | ERAS (n = 297) | P | ||||||||||||
Sex, male | 164 (40%) | 113 (38%) | 0.64 | ||||||||||||
Mean age, years (SD) | 68 (11) | 67 (10) | 0.22 | ||||||||||||
Mean weight, kg (SD) | 84 (19) | 87 (20) | 0.092 | ||||||||||||
Medical history | |||||||||||||||
Current smoker | 46 (11%) | 30 (10%) | 0.65 | ||||||||||||
Hypertension | 284 (69%) | 194 (65%) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||
Coronary artery disease | 70 (17%) | 41 (14%) | 0.25 | ||||||||||||
Stroke | 20 (5%) | 10 (3%) | 0.33 | ||||||||||||
Heart failure | 19 (5%) | 15 (5%) | 0.86 | ||||||||||||
Peripheral vascular disease | 13 (3%) | 8 (3%) | 0.72 | ||||||||||||
Diabetes | 81 (20%) | 73 (25%) | 0.12 | ||||||||||||
COPD | 88 (21%) | 67 (23%) | 0.70 | ||||||||||||
Preoperative anaemia | 36 (9%) | 22 (7%) | 0.52 | ||||||||||||
Usual medications | |||||||||||||||
Opioid | 106 (26%) | 58 (20%) | 0.053 | ||||||||||||
Aspirin within 5 days | 58 (14%) | 54 (18%) | 0.14 | ||||||||||||
Clopidogrel within 7 days | 2 (< 1%) | 0 | 0.23 | ||||||||||||
Warfarin within 7 days | 22 (5%) | 6 (2%) | 0.025 | ||||||||||||
NSAID/COX-2 inhibitor | 109 (26%) | 109 (37%) | 0.004 | ||||||||||||
ACE inhibitor/ARB | 235 (57%) | 168 (57%) | 0.90 | ||||||||||||
Beta blocker | 71 (17%) | 51 (17%) | 0.98 | ||||||||||||
Statin | 141 (34%) | 89 (30%) | 0.37 | ||||||||||||
Calcium channel blocker | 98 (24%) | 73 (25%) | 0.81 | ||||||||||||
Diuretic | 120 (29%) | 79 (27%) | 0.45 | ||||||||||||
Oral hypoglycaemic | 57 (14%) | 60 (20%) | 0.024 | ||||||||||||
Insulin | 9 (2%) | 11 (4%) | 0.25 | ||||||||||||
LMWH | 20 (5%) | 8 (3%) | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
ASA physical status | 0.57† | ||||||||||||||
1 | 10 (2%) | 10 (3%) | |||||||||||||
2 | 223 (54%) | 161 (54%) | |||||||||||||
3 | 172 (42%) | 122 (41%) | |||||||||||||
4 | 7 (2%) | 3 (1%) | |||||||||||||
Disease | 0.22 | ||||||||||||||
Osteoarthritis | 367 (89%) | 275 (93%) | |||||||||||||
Rheumatoid arthritis | 4 (1%) | ||||||||||||||
Avascular necrosis | 14 (3%) | 7 (2%) | |||||||||||||
Other | 27 (7%) | 15 (5%) | |||||||||||||
Previous PONV or motion sickness | 124 (30%) | 81 (27%) | 0.41 | ||||||||||||
ACE = angiotensin-converting enzyme. ARB = angiotensin-receptor blocker. ASA = American Society of Anesthesiologists. COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COX = cyclooxygenase. ERAS = enhanced recovery after surgery, LMWH = low molecular weight heparin. NSAID = non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. PONV = postoperative nausea and vomiting. * Data are no. (%) of patients unless otherwise specified. † P value derived from χ2 test for trend.
3 Perioperative and surgical care*
Variable | Existing practice (n = 412) | ERAS (n = 297) | P | ||||||||||||
Preadmission clinic, seen by: | |||||||||||||||
Nurse† | 406 (99%) | 297 (100%) | 0.037 | ||||||||||||
Anaesthetist | 405 (98%) | 297 (100%) | 0.024 | ||||||||||||
Surgeon | 406 (99%) | 297 (100%) | 0.037 | ||||||||||||
Physiotherapist† | 331 (80%) | 224 (75%) | 0.12 | ||||||||||||
Occupational therapist | 324 (79%) | 249 (84%) | 0.077 | ||||||||||||
Dietitian† | 0 | 61 (21%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Day of surgery | |||||||||||||||
Admission on day of surgery | 404 (98%) | 294 (99%) | 0.32 | ||||||||||||
Shower with antibiotic soap | 399 (97%) | 238 (80%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Preoperative skin wipes | 4 (1%) | 91 (31%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Oral (clear) fluids given† | 2 (< 1%) | 180 (61%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Oral carbohydrate drink† | 0 | 248 (84%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Gabapentin premedication† | 21 (5%) | 172 (58%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Type of surgery | |||||||||||||||
Hip | 214 (52%) | 129 (43%) | 0.025 | ||||||||||||
Knee | 198 (48%) | 168 (57%) | 0.025 | ||||||||||||
Revision | 26 (6%) | 13 (4%) | 0.26 | ||||||||||||
Tubes | |||||||||||||||
Urinary catheter | 200 (49%) | 107 (36%) | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Drain tube(s) | 105 (25%) | 59 (20%) | 0.080 | ||||||||||||
Type of anaesthesia | |||||||||||||||
General (± regional) | 266 (65%) | 164 (55%) | 0.014 | ||||||||||||
Spinal† | 236 (57%) | 205 (69%) | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Epidural or CSE | 16 (4%) | 3 (1%) | 0.019 | ||||||||||||
Postoperative regional analgesia | |||||||||||||||
Nerve block used | 135 (33%) | 44 (15%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
LA infiltration† | 214 (52%) | 222 (75%) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
PONV prophylaxis† | 233 (57%) | 202 (68%) | 0.002 | ||||||||||||
Mean total IV fluids, mL (SD)† | 1756 (767) | 1446 (687) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Active (forced air) warming† | 392 (95%) | 285 (96%) | 0.34 | ||||||||||||
Mean lowest temperature, °C (SD) | 35.7 (0.5) | 36.2 (0.4) | 0.039 | ||||||||||||
Mean duration of surgery, hours (SD) | 2.0 (0.9) | 1.9 (0.6) | 0.33 | ||||||||||||
CSE = combined spinal and epidural. ERAS = enhanced recovery after surgery. IV = intravenous. LA = local anaesthesia. PONV = postoperative nausea and vomiting. * Data are no. (%) of patients unless otherwise specified. † Key ERAS implementation points. | |||||||||||||||
4 Recovery profile and hospital stay
Variable | Existing practice (n = 412) | ERAS (n = 297) | P | ||||||||||||
Recovery room | |||||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), at rest* | 0 (0–5) | 0 (0–4) | 0.047 | ||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), on movement* | 0 (0–7) | 0 (0–4) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Admission temperature, °C (SD) | 36.1 (0.5) | 36.0 (0.6) | 0.006 | ||||||||||||
Postoperative, at 24 hours | |||||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), at rest* | 5 (3–7) | 4 (2–5) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), on movement* | 6 (4–8) | 5 (3–7) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Mean quality of recovery score (SD) (range, 0–150) | 103 (19) | 106 (20) | 0.056 | ||||||||||||
Total knee replacement | |||||||||||||||
Mean knee flexion (SD), degrees | 51 (19) | 57 (24) | 0.026 | ||||||||||||
Median quadriceps strength (IQR), Nm | 3 (2–3) | 2 (2–3) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||
Postoperative, at 48 hours | |||||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), at rest* | 4 (2–6) | 3 (1–5) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Median pain score (IQR), on movement* | 6 (4–8) | 5 (2–7) | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Total knee replacement | |||||||||||||||
Mean knee flexion (SD), degrees | 72 (19) | 78 (14) | 0.009 | ||||||||||||
Median quadriceps strength (IQR), Nm | 3 (2–3) | 3 (2–3) | 0.90 | ||||||||||||
Recovery parameters, median hours (IQR) | |||||||||||||||
Weight bearing | 1.1 (1.0–2.0) | 1.0 (0.9–2.0) | 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Oral fluid intake | 3.2 (2.0–5.0) | 2.7 (1.7–4.1) | 0.016 | ||||||||||||
Oral food intake | 7.0 (4.3–15) | 6.3 (3.2–7.9) | 0.004 | ||||||||||||
Removal of drain tubes | 27 (24–42) | 25 (23–27) | 0.002 | ||||||||||||
Removal of urinary catheter | 48 (42–76) | 33 (17–60) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Blood transfusion in hospital, no. of patients (%) | 58 (14%) | 31 (10%) | 0.24 | ||||||||||||
Return to theatre, no. of patients (%) | 14 (3%) | 10 (3%) | 0.76 | ||||||||||||
Length of stay, days | |||||||||||||||
Geometric mean (SD) | 5.3 (1.6) | 4.9 (1.6) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Median (IQR) | 5.0 (4.0–6.8) | 5.0 (3.8–6.2) | 0.10 | ||||||||||||
ERAS = enhanced recovery after surgery. IQR = interquartile range. * Visual analogue scale: 0 = none, 10 = severe. | |||||||||||||||
5 Recovery profile at 6 weeks after surgery*
Variable | Existing practice (n = 412) | ERAS (n = 297) | P | ||||||||||||
Wound infection | 21 (5%) | 13 (4%) | 0.99 | ||||||||||||
Prosthesis infection | 5 (1%) | 2 (< 1%) | 0.60 | ||||||||||||
Prosthetic joint dislocation | 2 (< 1%) | 3 (1%) | 0.31 | ||||||||||||
Periprosthetic fracture | 0 | 0 | > 0.99 | ||||||||||||
Thromboembolism | 13 (3%) | 10 (3%) | 0.59 | ||||||||||||
Urinary tract infection | 8 (2%) | 2 (1%) | 0.22 | ||||||||||||
Death | 2 (< 1%) | 1 (< 1%) | 0.85 | ||||||||||||
Worst pain rating in past 24 hours† | 2 (0–4) | 2 (0–3) | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
Extent of disability in past 24 hours† | 2 (0–3) | 1 (0–2) | 0.37 | ||||||||||||
Patient satisfaction‡ | |||||||||||||||
Was surgery worthwhile? | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–1) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Did surgery improve your daily life? | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | 0.015 | ||||||||||||
Do you feel better? | 1 (1–2) | 1 (1–2) | < 0.001 | ||||||||||||
Do you have trouble sleeping? | 3 (2–4) | 3 (2–4) | 0.67 | ||||||||||||
Hospital readmission | 25 (6%) | 15 (5%) | 0.87 | ||||||||||||
ERAS = enhanced recovery after surgery. * Data are no. (%) of patients or median score (IQR). † Visual analogue scale: 0 = none, 10 = severe. ‡ 5-point Likert scale: 0 = strongly agree, 5 = strongly disagree. | |||||||||||||||
Received 22 April 2014, accepted 22 October 2014
- Nicholas Christelis1,2
- Sophie Wallace1
- Claire E Sage1
- Uate Babitu3
- Susan Liew1
- James Dugal3
- Ibolya Nyulasi1,2
- Nora Mutalima4
- Ton Tran5
- Paul S Myles1
- 1 The Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, VIC.
- 2 Monash University, Melbourne, VIC.
- 3 Bendigo Hospital, Bendigo, VIC.
- 4 Dandenong Hospital, Melbourne, VIC.
- 5 Monash Health, Melbourne, VIC.
We thank the research and clinical staff of each of the three hospitals.
This project received funding from the Victorian Department of Health (Chris Potter, Senior Policy Officer). This included a payment to Paul Myles for protocol development, analysis and writing of a report.
- 1. March LM, Bagga H. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis in Australia. Med J Aust 2004; 180 (5 Suppl): S6-S10. <MJA full text>
- 2. Kehlet H, Mogensen T. Hospital stay of 2 days after open sigmoidectomy with a multimodal rehabilitation programme. Br J Surg 1999; 86: 227-230.
- 3. Starks I, Wainwright TW, Lewis J, et al. Older patients have the most to gain from orthopaedic enhanced recovery programmes. Age Ageing 2014; 43: 642-648.
- 4. Larsen K, Hvass KE, Hansen TB, et al. Effectiveness of accelerated perioperative care and rehabilitation intervention compared to current intervention after hip and knee arthroplasty. A before-after trial of 247 patients with a 3-month follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2008; 9: 59.
- 5. Malviya A, Martin K, Harper I, et al. Enhanced recovery program for hip and knee replacement reduces death rate. Acta Orthop 2011; 82: 577-581.
- 6. Ibrahim MS, Khan MA, Nizam I, Haddad FS. Peri-operative interventions producing better functional outcomes and enhanced recovery following total hip and knee arthroplasty: an evidence-based review. BMC Med 2013; 11: 37.
- 7. Kehlet H, Søballe K. Fast-track hip and knee replacement — what are the issues? Acta Orthop 2010; 81: 271-272.
- 8. Husted H, Jensen CM, Solgaard S, Kehlet H. Reduced length of stay following hip and knee arthroplasty in Denmark 2000-2009: from research to implementation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2012; 132: 101-104.
- 9. Stark PA, Myles PS, Burke JA. Development and psychometric evaluation of a postoperative quality of recovery score: the QoR-15. Anesthesiology 2013; 118: 1332-1340.
- 10. World Health Organization. International classification of functioning, disability and health. http://www.who.int/classifications/icf/en/ (accessed Oct 2014).
- 11. Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, et al. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2007; 11: R31.
- 12. Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, et al. Acute renal failure – definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 2004; 8: R204-R212.
- 13. Liu KD, Thompson BT, Ancukiewicz M, et al. Acute kidney injury in patients with acute lung injury: impact of fluid accumulation on classification of acute kidney injury and associated outcomes. Crit Care Med 2011; 39: 2665-2671.
- 14. Thompson EG, Gower ST, Beilby DS, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery program for elective abdominal surgery at three Victorian hospitals. Anaesth Intensive Care 2012; 40: 450-459.
- 15. Husted H, Lunn TH, Troelsen A, et al. Why still in hospital after fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop 2011; 82: 679-684.
- 16. Maessen J, Dejong CH, Hausel J, et al. A protocol is not enough to implement an enhanced recovery programme for colorectal resection. Br J Surg 2007; 94: 224-231.
- 17. Scott NB, McDonald D, Campbell J, et al. The use of enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) principles in Scottish orthopaedic units – an implementation and follow-up at 1 year, 2010-2011: a report from the Musculoskeletal Audit, Scotland. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2013; 133: 117-124.
- 18. Garson L, Schwarzkopf R, Vakharia S, et al. Implementation of a total joint replacement-focused perioperative surgical home: a management case report. Anesth Analg 2014; 118: 1081-1089.





Abstract
Objective: To institute and evaluate the benefits of an enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) program across three hospitals in Victoria.
Design, setting and participants: We used a before-and-after quality improvement study design consisting of three phases: pre-ERAS program data collection from March to September 2012; ERAS training and implementation during September 2012; and change performance measurement following ERAS implementation from October 2012 to May 2013.
Main outcome measures: The primary end point was duration of hospital stay after knee or hip arthroplasty. Secondary end points were adherence to the ERAS bundle, and process and patient recovery characteristics.
Results: We enrolled 412 patients to the pre-ERAS (existing-practice) phase and compared them with 297 patients in the ERAS phase. For ERAS patients, compared with existing-practice patients, hospital stay was reduced (geometric mean, 5.3 [SD, 1.6] v 4.9 [SD, 1.6] days; P < 0.001) and there was a significant improvement in the proportion of patients ready for discharge on Day 3 after surgery (41% v 59%; P < 0.001). The most common reason for delayed discharge was patients waiting for review or access to rehabilitation services. There were markedly improved indicators of processes and outcomes of care, including improved patient education, reduced fasting times, less blood loss, better analgesia, earlier ambulation and improved overall quality of recovery.
Conclusion: We found that an ERAS program could be successfully implemented in elective joint arthroplasty, leading to a shorter duration of hospital stay. We recommend this orthopaedic ERAS pathway.